SchemaRD
Overview
SchemaRD is a Entity Relationship Diagram Viewer for schema.rb which is used on Ruby On Rails. You can browse Entity Relationship Diagram of your schema.rb, on your WebBrowser.
How To Use
Install:
$ gem install schemard
And run:
$ schemard
And browse http://localhost:10080
How To Edit ERD
Edit Layout
In the ERD generated by default, the tables are laid out at random.
The figure below is the table schema which has generated from schema.rb of the Ruby On Rails Tutorial( https://www.railstutorial.org/ ).
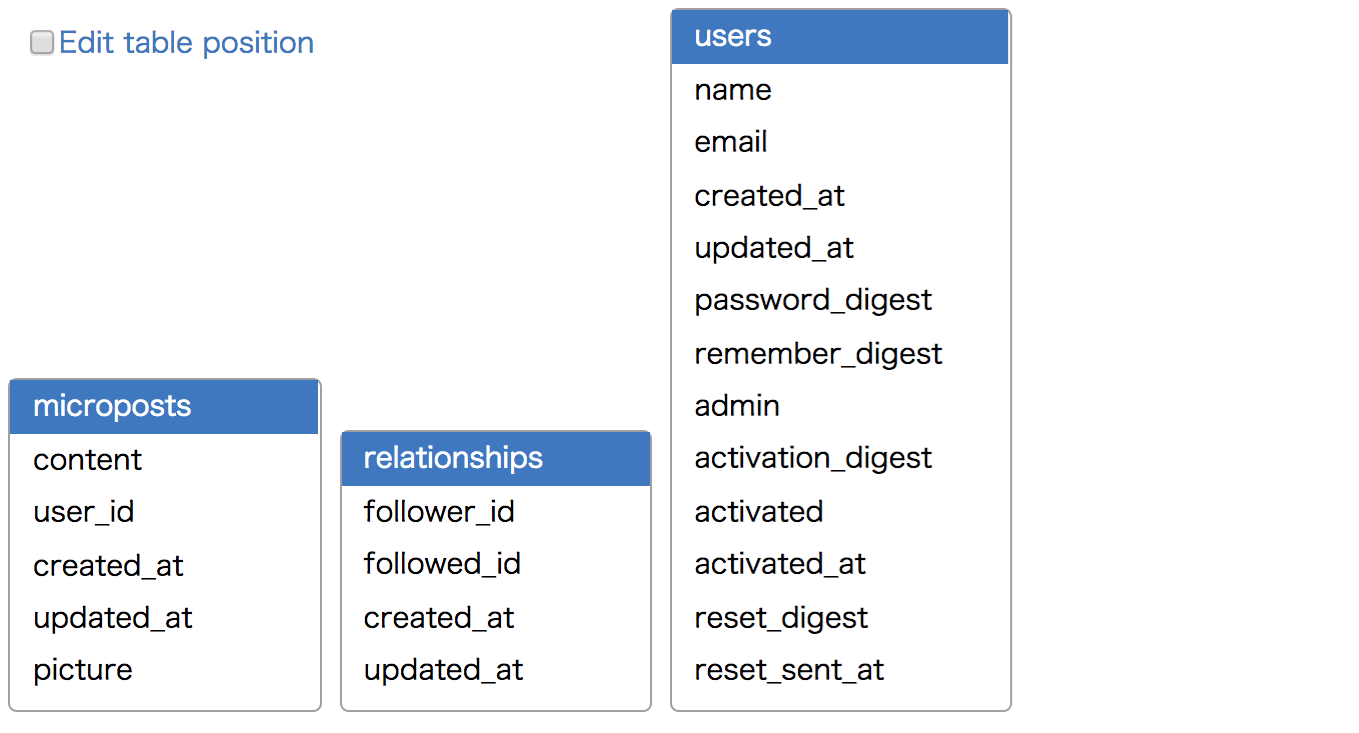
To layout tables in desired position, You can adjust the position by checking "Edit table position" at the top left of the figure,
And dragging the table.
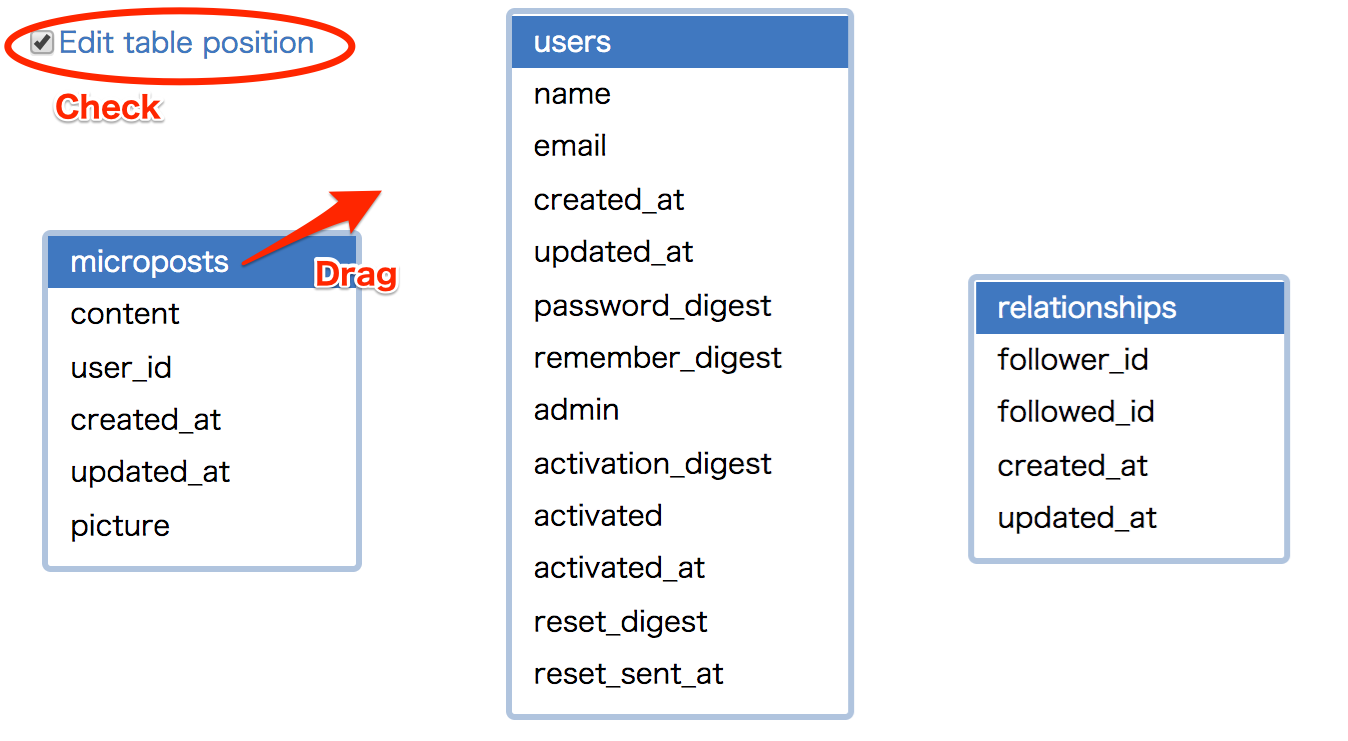
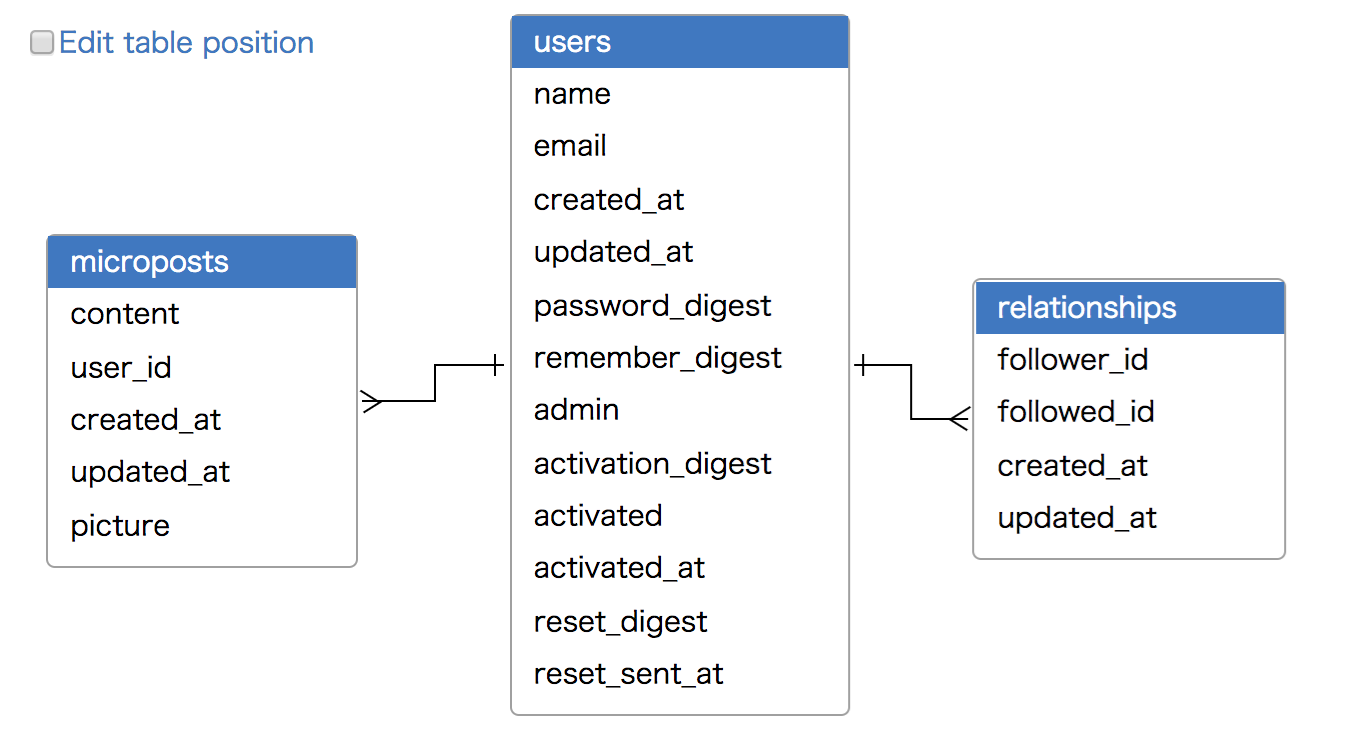
To finish layout for tables, you check to off "Edit table position".
Add Relation
In the ERD generated by default, there is no relation information between tables.
To add a relation to the ERD, You need to create relation information separately from "schema.rb",
and load it. There are several ways to give a relation information.
This section explains how to add relation information based on model information of Rails application. Just as before, we will explain the procedure with the source code of Ruby On Rails Tutorial.
Extract relation information with the following command. In this example, it outputs to
db/relatoin.metadata.$ cd <Rails.root.dir> $ schemard gen-relation > db/relation.metadataThe following contents are output to
db/relatoin.metadata.--- tables: users: has_many: - microposts - relationships - relationships relationships: belongs_to: - users - users microposts: belongs_to: - usersTo load the extracted relationship information, execute with the following
-fcommand option.$ schemard -f db/relation.metadataThe extracted relationship information have been added to the ERD, when accessing
http://localhost:10080in the Web browser.
Localization
In the ERD generated by default, physical names are displayed as the table name and column name.
There are several ways to display aliases other than physical names as table names and column names,
This section explains the procedure to use the translation file for ActiveRecord.
- There is a translation file placed to
config/locale/ja.yml, and it have contents below ``` ja: activerecord: models:: <モデル名>
ja:
activerecord:
attributes:
2. Specify the translation file with the -f option and execute it as follows
$ schemard -f db/relation.metadata -f config/locale/ja.yml
## Options
The following command line options can be specified.
* -i, --input-file ... Specify the `schema.rb` file. The default is `db/schema.rb`.
* -o, --output-file ... Specify the file to output layout information. The default is `schema.metadata`.
* -f, -m, --metadata-file ... Specify the file of Relation information file, or translation file. The default is no specification.
* --rdoc, --rdoc-enabled ... It is specified when acquiring meta-information from rdoc-format comment described in `schema.rb`. The default is no specification.
* --parse-db-comment-as ... Specify how to interpret the comment option in the migration information. `name`,`ignore` can be specified. When `name` is specified, the value specified by the comment option is interpreted as a logical name. `ignore` ignores the value of the comment option. The default is `ignore`.
* -l, --log-output ... Specify the log output destination. `stdout`,`stderr`, `<file name>` can be specified. The default is `stdout`.
* -s --silent --no-log-output ... Specify this when you do not want log output.
* -h, -host ... Specify the host name that WebServer listens on. The default is `127.0.0.1`.
* -p, --port ... Specify the port that WebServer listens on. The default is `10080`.
### Sub Command
The following sub-commands can be specified.
* generate-relations ... Extract relation information from model information of Rails application and output it to standard output in YAML format. You can specify the Rails.root directory with the `-d` option (the default is the current directory).
## Configuration
Instead of specifying it with command line options, you can specify options in the configuration file.
Place the configuration file as `.schemard.config` in the` schemard` command execution directory. The following entries can be specified.
* input_file
* output_file
* metadata_files
* rdoc_enabled
* parse_db_comment_as
* log_output
* webserver_host
* webserver_port
If both the setting file and the command line option are specified, the command line option takes precedence.